What is insulin?
Insulin is a natural hormone produced by the beta cells in the pancreas that helps to regulate blood sugar levels. The insulin producing beta cells monitors the blood sugar to ensure it is constant. If your blood glucose increases after taking carbohydrate foods, your body will stimulate the beta cells to produce insulin. Insulin controls blood glucose by signaling the fat and muscle cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream. This process helps to reduce high blood glucose levels. In case the body cannot naturally produce insulin or becomes resistant to it, you may develop symptoms of diabetes.
What is glucose?
Glucose is a form of sugar that is also known as blood glucose. It is the main source of energy that is required by our body to function properly. Glucose is found in foods such as dried fruits, potatoes, pasta, and bread. Glucose is usually absorbed into the body via digestion. When you eat foods that are rich in carbohydrates, it moves from the mouth to stomach before ending up in the small intestines. The stomach and the small intestines will absorb and release glucose into the bloodstream. Once in the bloodstream, the natural hormone insulin will help glucose enter the body cells.
The relationship between insulin and glucose in diabetes
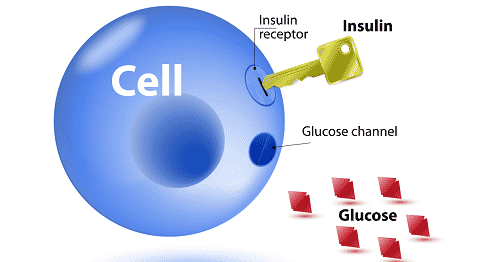
Glucose and insulin relationship. The natural hormone insulin plays a big role in helping glucose enter the body cells for fuel. Without insulin, glucose cannot enter the body cells. This is because glucose is too thick to penetrate the cell membrane. As a result, they stay in the bloodstream. When the level of blood glucose rises, the body will signal the pancreas to release insulin into the bloodstream. Normally, insulin attaches itself to the insulin receptors outside the body cells. This opens the gateway for glucose to enter the cells for fuel. In healthy people, they can naturally produce insulin. Thus, they are able to convert blood glucose into energy. However, patients with diabetes mellitus cannot produce enough insulin. Hence, they experience high blood glucose levels. If the level of blood glucose is not properly controlled, it may lead to long-term health problems such as nerve damage and kidney problems. Patients with type 1 diabetes require insulin medications so that they can survive.
Low blood glucose
In case your blood glucose level is too low, you may experience a condition known as hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia usually occurs in diabetic patients who take insulin medication. However, it may also occur in other people, especially when you stay too long before taking a meal or after heavy exercise. If you are diabetic, it is important you monitor your blood glucose regularly and you follow your treatment program. Any adjustment to your treatment program without your doctor’s permission can adversely affect your blood glucose levels. When blood glucose levels fall below 70 mg/dL your body cells cannot function properly.
As a result, you may develop symptoms of hypoglycemia such as:
- Sweatiness
- Hunger
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Shakiness
If you notice any of the above symptoms, you should call your doctor for medical advice. Otherwise, it is advisable you carry glucose tablets that come in 15 gm packet. A glucose tablet is a simple carbohydrate that helps to increase blood sugar levels when it falls below the normal level. If hypoglycemia is not treated, it may become severe, leading to serious conditions such as seizure or coma. In this case, you may require glucagon kit. A glucagon kit is available when prescribed by a doctor. Speak to your doctor to find out if you need a glucagon kit.
Doctor’s Recommendation
Insulin and glucagon help control blood sugar levels. Insulin helps cells absorb glucose from the blood, while glucagon signals the liver to release glucose. People with type 1 diabetes need extra insulin to keep their blood sugar levels from getting too high. For type 2 diabetes, doctors usually suggest diet and exercise first, but insulin may also be needed. If blood sugar gets too low, glucagon may be necessary, as very low blood sugar can be dangerous without treatment.