Ever stopped to consider the lifeline of diabetes management? Amidst the daily juggle of medications, dietary choices, and exercise routines, one vital aspect often takes center stage: monitoring blood glucose levels. But why is this practice so crucial? How does it truly impact the management of diabetes? Let’s dive deeper into the significance of understanding blood glucose monitoring and its pivotal role in empowering you to take charge of your health journey.
Glucose Levels: What You Need to Know
Glucose, also known as blood sugar, serves as the primary fuel for your body, providing energy for essential functions ranging from physical activity to cognitive processes. When you consume carbohydrates through foods like bread, pasta, fruits, and vegetables, your digestive system breaks them down into glucose molecules. After digestion, glucose molecules are absorbed into the bloodstream and circulated throughout the body, providing fuel for cells.
In individuals without diabetes, the body’s intricate system of hormones, primarily insulin, works seamlessly to regulate blood glucose levels. The pancreas creates insulin, which works like a key to open cells and lets glucose in for energy. Extra glucose gets stored in the liver or muscles until the body needs it.
Yet, if you have diabetes, this delicate balance is disturbed. In Type 1 diabetes, the immune system unknowingly attacks and impairs the pancreas cells responsible for producing insulin, resulting in insufficient insulin production. In Type 2 diabetes, the body acquires resistance to insulin’s effects, or there may not be enough insulin produced to meet the body’s requirements.
Why Is It Important to Monitor Glucose Closely?
Monitoring blood sugar is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it provides significant insights into how your body handles sugar, indicating whether adjustments to your treatment plan are necessary. Secondly, it helps you avoid immediate issues like low blood sugar and long-term complications such as nerve damage and heart problems.
Furthermore, closely watching your blood sugar levels enables you to make informed decisions about your lifestyle and medication. By tracking how your blood sugar levels change over time, you can pinpoint patterns and adapt your diet, physical activity, and medication schedule accordingly. It is an integral part of effective diabetes management, empowering you to lead a healthy and fulfilling life despite the challenges triggered by the condition.
How to Monitor Your Blood Glucose
Monitoring blood glucose levels can be done through various methods. These diverse approaches help you to choose the monitoring method that best suits your lifestyle and preferences, ensuring comprehensive oversight of your blood sugar levels.
Home Blood Glucose Meters
These portable devices are a convenient tool for you to monitor your blood sugar regularly in the comfort of your own home. By using a small drop of blood obtained from a finger prick, these diabetic meters provide immediate feedback on current blood sugar levels. It’s recommended to check blood sugar levels at key times throughout the day, such as before and after meals, as well as before and after physical activity.
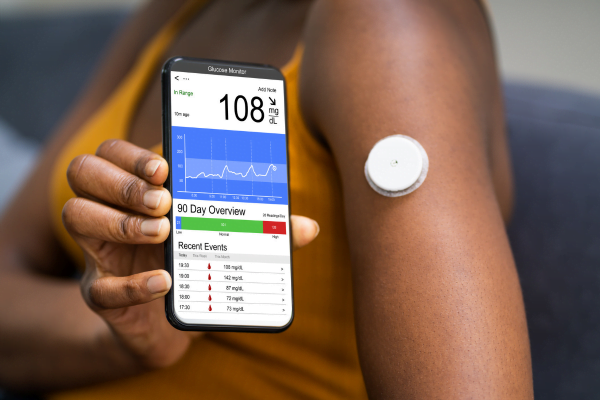
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems
CGM systems utilize a tiny sensor placed beneath the skin to measure and determine glucose levels in the interstitial fluid continuously. These sensors transmit real-time glucose readings to a receiver or smartphone app, allowing you to track your glucose levels all day and night. With the best CGM technology, you can say goodbye to frequent finger pricks and gain valuable insights into your glucose fluctuations for optimized diabetes management.
A1C Test
The A1C test, also recognized as the glycated hemoglobin test, offers a comprehensive assessment of blood sugar control over the past two to three months. Unlike the immediate feedback provided by home blood glucose meters, the A1C test measures the average blood glucose levels over a more expanded period. Healthcare professionals typically administer this test during regular check-ups to evaluate long-term diabetes management.
Urine Glucose Testing
While less common than other methods, urine glucose testing offers an alternative for blood sugar monitor without finger pricks. It involves using test strips to measure the presence of glucose in the urine. This method provides an indirect assessment of blood glucose levels but is not as accurate or reliable as other monitoring methods. Urine glucose testing may be used in certain situations where blood glucose monitoring is not feasible or as a supplementary tool for diabetes management.
Managing Glucose Levels
Effective management of blood glucose levels involves a combination of regular monitoring, healthy lifestyle choices, medication adherence, regular exercise, and dietary modifications. By collaborating closely with healthcare providers and adhering to a customized diabetes management strategy, you can aim to reach and maintain desired blood glucose levels.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What should blood sugar be at bedtime?
Blood sugar levels at bedtime should ideally be within the range of 90 to 150 mg/dL for most individuals with diabetes. It’s essential to monitor your blood sugar regularly, especially with at-home diabetes tests, to ensure it stays within the recommended range for optimal health.
What is the best A1C home test kit?
The best A1C home blood sugar test kit is subjective and may vary according to specific individual preferences and needs. However, popular options include kits from reputable brands like Bayer, Accu-Chek, and A1CNow. It’s essential to choose a kit that is accurate, easy to use, and provides reliable results to monitor your long-term blood sugar control effectively.
How to lower A1C quickly before blood tests?
To lower A1C quickly before blood tests, focus on making immediate lifestyle changes, including adopting a balanced diet, increasing physical exercise, and managing stress levels. Additionally, ensure adherence to prescribed medications and consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
How long after taking insulin should I check blood sugar?
It’s recommended to check blood sugar levels around 2 hours after taking insulin, as this allows sufficient time for the medication to take effect. Utilizing a home test for diabetes enables you to monitor your blood sugar levels comfortably and promptly after insulin administration.