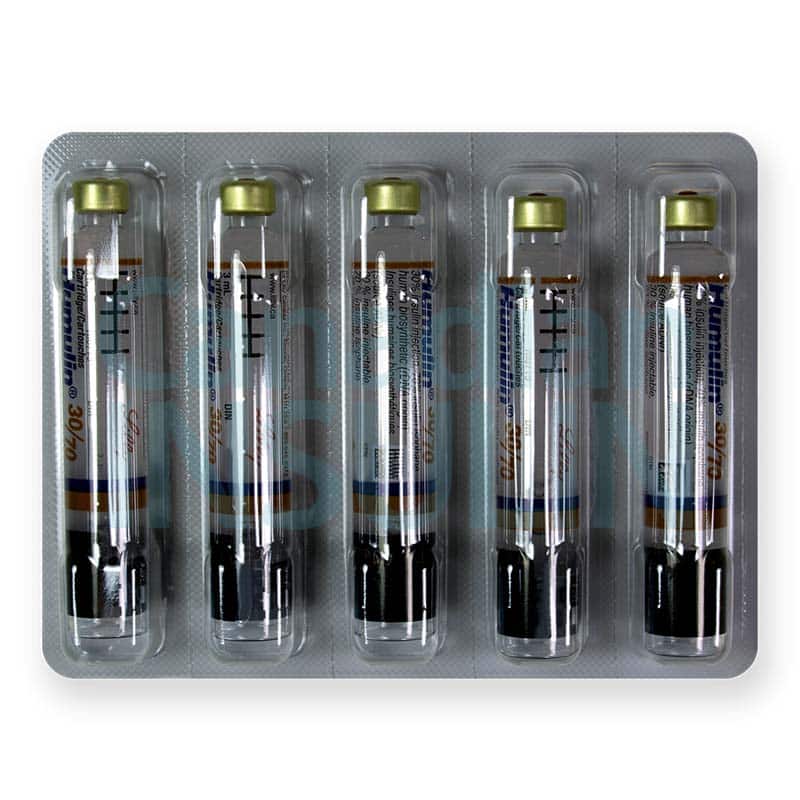
Please note: a valid prescription is required for all prescription medication.
Humulin 30/70 Cartridges Product Overview and Safety
Also available for your pet.
Offer extended: Use code SAVE10 for 10% OFF all RX meds now through March 10, 2026. Ozempic from Canada and Mounjaro Vial not included. Coupon code cannot be combined with other offers. For products with “Bulk Savings”, the discount will be applied to the regular price for 1 unit. Maximum allowable quantity equal to a 90 day supply per single order.
$79.99
You save


Humulin 30/70 Cartridges are a premixed human insulin used to help manage blood glucose in diabetes. The cartridge format is intended for use with compatible reusable insulin pens. This page explains how the mix works, practical handling basics, and key safety points to review with a clinician.
What Humulin Cartridges Is and How It Works
This medicine is a biphasic insulin mix, meaning it combines two types of human insulin in one cartridge. It typically includes regular insulin (shorter-acting mealtime insulin) plus isophane insulin (NPH; intermediate-acting insulin) to cover both meal-related rises and background needs. After injection under the skin, the regular component starts working sooner, while the NPH component is absorbed more slowly to extend effect. Many people encounter it labeled as a Humulin 70/30 cartridge or Huminsulin 30/70 cartridge, depending on regional naming conventions and labeling.
In terms of process, the service can help route prescription information for review, while licensed pharmacies dispense where permitted. Some patients explore Ships from Canada to US when cross-border fulfilment is appropriate for their situation. For broader context on treatment options, the Pre Mixed hub can help you browse similar premixed insulin categories.
Who It’s For
Premixed human insulin may be prescribed for people with Type 1 Diabetes or Type 2 Diabetes when a clinician determines a fixed-ratio combination fits the treatment plan. It can be considered when consistent meal timing and carbohydrate patterns are feasible, because the mix provides both mealtime and intermediate coverage together. Some people use premixed insulin to reduce the number of daily injections compared with a multi-injection basal-bolus plan, though that tradeoff is not appropriate for everyone.
Humulin 30/70 Cartridges are not used to treat diabetic ketoacidosis (a medical emergency that requires different insulin management). They should also not be used during episodes of low blood sugar, and they are avoided in people with a known allergy to insulin human or other ingredients in the formulation. If a person has recurrent hypoglycemia, major changes in eating patterns, or a history of severe reactions, clinicians usually reassess whether a premixed regimen is the best match.
Dosage and Usage
Dosing schedules for premixed human insulin are individualized by the prescriber based on glucose patterns, meals, activity, and other medicines. Many premixed regimens are taken once or twice daily before meals, but the timing and frequency depend on the plan and the product label. Clinicians may recommend checking glucose at specific times to understand both meal-related peaks and overnight trends; the guide Monitor Blood Sugar summarizes common monitoring considerations people discuss with their care team.
When using Humulin 30/70 Cartridges with a reusable pen, follow the device instructions for inserting the cartridge, attaching a new needle, and priming before each injection. Rotate injection sites to reduce skin changes, and do not share pens or needles. This premix is a suspension, so gentle mixing is often required per the product instructions to ensure a uniform, cloudy appearance; avoid vigorous shaking unless the label specifically instructs it. If the suspension looks clumpy, has particles stuck to the cartridge wall, or does not re-suspend evenly, the cartridge should not be used.
Quick tip: Confirm your pen model is compatible with the cartridge system before first use.
Meals and activity can strongly affect glucose outcomes with premixed insulin. Clinicians often emphasize consistent meal timing and planned carbohydrate intake; the resource Best Diet Insulin Resistance provides general nutrition concepts many patients review alongside medication plans.
Strengths and Forms
Premixed human insulin cartridges are commonly available in U-100 concentration (100 IU/mL), though availability can vary by country and pharmacy supply. Humulin 30/70 Cartridges are designed for pen-based injection using a compatible reusable pen device rather than a disposable prefilled pen. The product is a cloudy insulin suspension, reflecting the NPH component. Because it is a fixed mix, it is generally not intended to be combined with other insulins in the same injection unless the prescribing information explicitly allows it.
Labeling and naming can differ across markets. You may see descriptions such as Humulin 70 30 penfill, human insulin 70/30 cartridge, or isophane regular insulin 70/30 cartridge when the same concept is referenced. The key practical point is to verify the exact product name, concentration, and cartridge type on the box and cartridge label before use.
| Form | What it means in practice |
|---|---|
| Cartridge for reusable pen | Inserted into a compatible pen; new needle used for each injection. |
| Premixed suspension | Needs gentle re-suspension per label so dosing is consistent. |
| U-100 concentration | Standard concentration for many insulin pens; confirm on label. |
Storage and Travel Basics
Unopened insulin is usually stored refrigerated and protected from freezing and direct heat. For in-use cartridges, storage rules can differ by product and environment, including how long a cartridge may be kept at room temperature once started. Because these details are label-specific, it is safest to rely on the carton and package insert for exact temperature ranges and in-use time limits. Keep insulin away from direct sunlight and avoid leaving it in a hot car, a checked suitcase, or near freezing temperatures.
If Humulin 30/70 Cartridges are carried during daily activities or travel, use an insulated container to reduce temperature extremes, but avoid placing the insulin directly against ice or freezer packs. Inspect the suspension before each injection; it should look uniformly cloudy after appropriate mixing steps. If there are persistent clumps, frosting, or signs of freezing, discard the cartridge and use a new one.
Why it matters: Temperature damage can reduce insulin reliability even when the label looks intact.
When traveling, keep supplies together: extra needles, alcohol swabs if used, a backup glucose meter or sensors as appropriate, and a sharps container plan. If crossing time zones, clinicians often help align meal timing and monitoring to reduce unexpected lows or highs.
Side Effects and Safety
Like other insulins, Humulin 30/70 Cartridges can cause hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), which is the most important safety risk to understand. Symptoms can include sweating, shakiness, hunger, headache, confusion, irritability, or sleepiness, and severe episodes can lead to loss of consciousness or seizures. Carrying a fast-acting carbohydrate source is commonly discussed in diabetes education, but the exact plan should match the clinician’s guidance, especially for people with reduced awareness of hypoglycemia.
Other possible side effects include injection-site reactions (redness, swelling, itching), weight gain, and edema (fluid retention). Repeated injections in the same area can contribute to lipohypertrophy (fatty lump under the skin), which may change absorption; rotating sites helps lower this risk. Serious but less common risks can include systemic allergic reactions and hypokalemia (low potassium), particularly in higher-risk settings. Seek urgent evaluation for signs of a severe allergic reaction such as widespread rash, trouble breathing, or facial swelling.
Extra caution is often needed during illness, reduced food intake, vomiting, or changes in physical activity, because insulin requirements can shift. Clinicians may recommend more frequent glucose checks during these periods and may adjust the overall plan rather than making ad hoc changes.
Drug Interactions and Cautions
Many medicines can affect blood glucose or change how insulin needs present day to day. Other glucose-lowering therapies may increase the risk of hypoglycemia when combined with insulin, especially when meals are delayed. Some drugs can mask typical low-blood-sugar symptoms; beta blockers are a well-known example. Corticosteroids, some diuretics, thyroid hormones, and certain psychiatric medicines can raise glucose, potentially increasing insulin requirements under clinician supervision.
Alcohol can contribute to delayed hypoglycemia in some situations, particularly when food intake is low. Kidney or liver impairment may change insulin clearance and increase the risk of low blood sugar, so clinicians often monitor closely. If you use multiple diabetes medicines, the explainer Common Diabetes Medications can help frame why combinations require planning and monitoring. Always share a current medication list with the prescriber, including over-the-counter products and supplements.
A specific caution applies to thiazolidinediones (TZDs): when used with insulin, they can worsen fluid retention and may contribute to heart failure in susceptible individuals. Clinicians generally weigh risks and benefits and monitor for swelling or shortness of breath.
Compare With Alternatives
Premixed human insulin is one of several ways to structure insulin therapy. Compared with a basal-bolus regimen (separate long-acting plus rapid-acting insulin), a premix can reduce the number of injections but offers less flexibility to adjust mealtime and background components independently. Compared with premixed insulin analogs, human premixes typically have different onset and meal timing characteristics, which can matter for people with variable schedules.
If Humulin 30/70 Cartridges do not fit meal timing, work shifts, or hypoglycemia risk, clinicians may discuss other approaches. For some people with type 2 diabetes, non-insulin injectable options may be considered as part of an overall plan, such as Ozempic Semaglutide Pens or Victoza Pens, depending on clinical goals and contraindications. Oral medicines also play a role for many patients; the overview Diabetes Medications List provides a neutral map of common classes people may hear about.
Switching between insulin types should be done with a prescriber’s plan, because timing, monitoring frequency, and dose equivalence can differ. When comparing options, it helps to consider lifestyle fit, hypoglycemia history, and ability to monitor and respond to changing glucose patterns.
Pricing and Access
Access to insulin cartridges depends on having a valid prescription and selecting the correct product, concentration, and cartridge system for the intended pen. For Humulin 30/70 Cartridges, coverage rules can vary by plan and jurisdiction, and some people also evaluate cash-pay options when coverage is limited. If you are without insurance, it can be useful to gather your prescription details, recent medication history, and any plan documentation before exploring options.
As part of a referral workflow, prescription details may be confirmed with the prescriber before a partner pharmacy fulfils, where permitted. Cross-border arrangements can involve additional eligibility checks and documentation requirements, and not every situation qualifies. If medication affordability is a concern, the resource Low Income Prescription Help outlines common steps patients discuss with clinics and payers.
When reviewing access considerations, it helps to clarify what training and supplies are needed for the cartridge-and-pen setup, including compatible pen hardware, needles, and sharps disposal. For broader educational reading on diabetes care topics, you can browse Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes article hubs.
Authoritative Sources
The most reliable dosing, compatibility, and storage instructions come from the product’s prescribing information and device instructions. Diabetes standards of care are also useful for understanding how insulin fits into a broader management plan, including monitoring and hypoglycemia prevention. Use these sources to support discussions with a licensed clinician who knows the full medical history.
For primary references, consider reviewing these materials directly:
- Manufacturer prescribing information in this document: Humulin 70/30 US Prescribing Information
- Clinical standards updated regularly are published here: Diabetes Care Journal Issues
When a licensed partner pharmacy dispenses, transport may use prompt, express, cold-chain shipping when required.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Express Shipping - from $25.00
Shipping with this method takes 3-5 days
Prices:
- Dry-Packed Products $25.00
- Cold-Packed Products $35.00
Standard Shipping - $15.00
Shipping with this method takes 5-10 days
Prices:
- Dry-Packed Products $15.00
- Not available for Cold-Packed products
Is Humulin 30/70 the same as Humulin 70/30?
They refer to the same concept: a premixed human insulin containing regular insulin plus NPH (isophane) insulin in a fixed ratio. Different regions may display the ratio in opposite order (30/70 vs 70/30) based on labeling conventions, but the clinical idea is the same mixture of short-acting and intermediate-acting components. Because packaging, device compatibility, and instructions can vary by market, it’s important to confirm the exact label text, concentration (often U-100), and cartridge format before use.
How does a premixed 30/70 insulin work compared with separate injections?
A premixed 30/70 insulin provides two action profiles in one injection: a faster component that covers meals and an intermediate component that supports between-meal and overnight glucose. With separate injections (often called basal-bolus), the long-acting and mealtime insulins can be adjusted independently, which may offer more flexibility for variable eating and activity. Premixes can simplify routines for some people but can be less adaptable when schedules change. Your prescriber determines which structure best matches glucose patterns and lifestyle.
Can Humulin 30/70 cartridges be used in any insulin pen?
Not all reusable insulin pens accept the same cartridge design. Cartridges are typically made for specific pen systems, and using an incompatible pen can lead to dosing errors or device malfunction. Before starting, check the cartridge label, the pen manufacturer’s compatibility list, and the instructions for use. Also confirm that the pen is designed for U-100 insulin if the cartridge is U-100. If there is any uncertainty, a pharmacist or diabetes educator can help verify compatibility and demonstrate correct loading and priming steps.
What are the most important safety issues to monitor with premixed insulin?
Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) is the key safety risk with any insulin, including premixed formulations. Learn typical symptoms (sweating, tremor, confusion) and discuss an action plan with your clinician. Injection-site reactions and lipohypertrophy (lumps from repeated injections) can occur; rotating sites helps. During illness, reduced appetite, vomiting, or unusual activity, insulin needs may change and closer glucose monitoring is often recommended. Seek urgent care for signs of severe allergy or inability to treat low blood sugar safely.
What should I ask my clinician before starting or switching to a 30/70 premix?
Useful questions include: what meal timing is assumed by the regimen; when to check glucose to capture both meal and overnight patterns; what to do if meals are delayed; and how to handle sick days or reduced intake. It also helps to confirm the exact product name, concentration, and cartridge-pen compatibility, plus how to mix the suspension correctly. If you take other diabetes medicines (including GLP-1 or SGLT2 drugs), ask how the combination affects hypoglycemia risk and monitoring frequency.
How should I store premixed insulin cartridges and what should I look for before injecting?
Storage instructions are label-specific, but unopened insulin is usually refrigerated and protected from freezing and heat. In-use cartridges may have room-temperature limits and time limits once started, so check the package insert. Before injecting, a premixed suspension should re-suspend evenly to a uniform cloudy look after the recommended mixing steps. Do not use a cartridge that appears frozen, has persistent clumps, shows particles stuck to the cartridge wall, or does not mix uniformly. When in doubt, replace it and consult a pharmacist.
Rewards Program
Earn points on birthdays, product orders, reviews, friend referrals, and more! Enjoy your medication at unparalleled discounts while reaping rewards for every step you take with us.
You can read more about rewards here.
POINT VALUE
How to earn points
- 1Create an account and start earning.
- 2Earn points every time you shop or perform certain actions.
- 3Redeem points for exclusive discounts.
You Might Also Like
Related Articles
Ozempic Side Effects In Females: Symptoms, Risks, Next Steps
Overview Ozempic (semaglutide) is a GLP-1 receptor agonist medication used for type 2 diabetes. Some people also discuss it in the context of weight management. This article focuses on ozempic…
Zepbound Side Effects Long-Term: What to Monitor Over Time
Key Takeaways Most effects are gastrointestinal and often improve over time. You may notice symptoms soon after the first injection. Track patterns: timing, triggers, and recovery after each dose. zepbound…
GLP-1 Drugs for Weight Loss: Options, Risks, and Next Steps
Key Takeaways These medicines target appetite signals and digestion to support weight management. Approval and use vary by product, condition, and country-specific labeling. Many options are injections; one GLP-1 medicine…
SGLT2 Inhibitors Mechanism of Action in Heart Failure
Overview Heart failure is not just a “weak heart.” It is a body-wide syndrome that affects fluid balance, kidneys, and energy use. Understanding sglt2 inhibitors mechanism of action in heart…