Managing diabetes at home requires clear steps, reliable habits, and steady follow‑up. Insulin for pets helps control blood glucose and reduce clinical signs, but daily routines matter as much as prescriptions. This guide explains how insulin works, what to expect, and how to partner with your veterinary team. It focuses on practical skills you can apply right away.
Key Takeaways
- Consistent routine: Fixed feeding times and injections support stable glucose.
- Right product: Insulin type, syringe, and needles must match exactly.
- Safe technique: Calm handling and proper sites reduce injection problems.
- Ongoing checks: Home observations and labs guide veterinary adjustments.
Insulin for Pets: When and Why It’s Used
Dogs and cats develop diabetes mellitus when the pancreas makes too little insulin or tissues resist its action. Without replacement insulin, glucose builds up and cells cannot use energy efficiently. Clinical signs include thirst, frequent urination, increased appetite, and weight loss. Veterinary evaluation confirms the diagnosis using blood glucose, fructosamine, and urinalysis.
Insulin therapy helps lower blood glucose and reduce symptoms, but it requires a structured plan. Vets tailor dose, product, and schedule to each pet’s needs. They also consider concurrent conditions such as pancreatitis, obesity, or infections that can destabilize control. Good communication between owners and the clinic is essential for safe long‑term care.
Understanding Diabetes in Dogs and Cats
In simple terms, insulin acts as a key that lets glucose move from blood into cells. When that key is missing or not working, glucose remains high (hyperglycemia). Over time, high glucose can dehydrate pets and strain organs. You may notice lethargy, cloudy eyes in some dogs, or poor coat quality in cats. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can reduce these effects.
Clinically, dogs often have insulin deficiency, while many cats show insulin resistance from concurrent disease. Your vet may discuss pathophysiology and monitoring plans using glucose curves and fructosamine. These tests track control over time and help detect patterns. Consistency with timing, diet, and activity supports more predictable results.
Types of Veterinary Insulin and Choosing Options
Veterinarians select insulin based on onset, peak, and duration (pharmacokinetics). Intermediate‑acting and long‑acting options are common, and species differences matter. Your vet may recommend porcine insulin zinc suspension or protamine zinc insulin (PZI) for dogs or cats. Cats often respond well to long‑acting analogs. Matching the insulin type to lifestyle and meal timing supports steadier glucose.
Some dogs use Humulin N insulin for dogs under veterinary supervision, while certain cats may do better on glargine. For PZI information, including labeled strength and handling, see ProZinc Vial for product specifics and composition details.
For background on NPH choices in canine care, review Humulin N Guide as an extended overview and comparison. Owners focused on canine therapy can also consult Insulin for Dogs for general concepts and monitoring ideas.
Dosing Basics, Monitoring, and Vet Protocols
Your veterinarian sets the starting dose and schedule based on weight, exam findings, and lab data. They will adjust over time using clinical signs, glucose curves, and periodic fructosamine. Home logs of appetite, water intake, urination, and activity add critical context. Avoid changing dose on your own; call the clinic before any adjustment.
Reference tools like a dog insulin dosage chart by weight may appear online, but they cannot replace individualized veterinary plans. Apps and calculators can help track routines, yet clinical decisions still depend on measured glucose and trends. For safety planning and error prevention, see Pet Insulin Dosage to learn common mistakes and how to avoid them. If your cat’s readings drift high between checks, Hyperglycemia In Cats explains patterns to discuss with your vet.
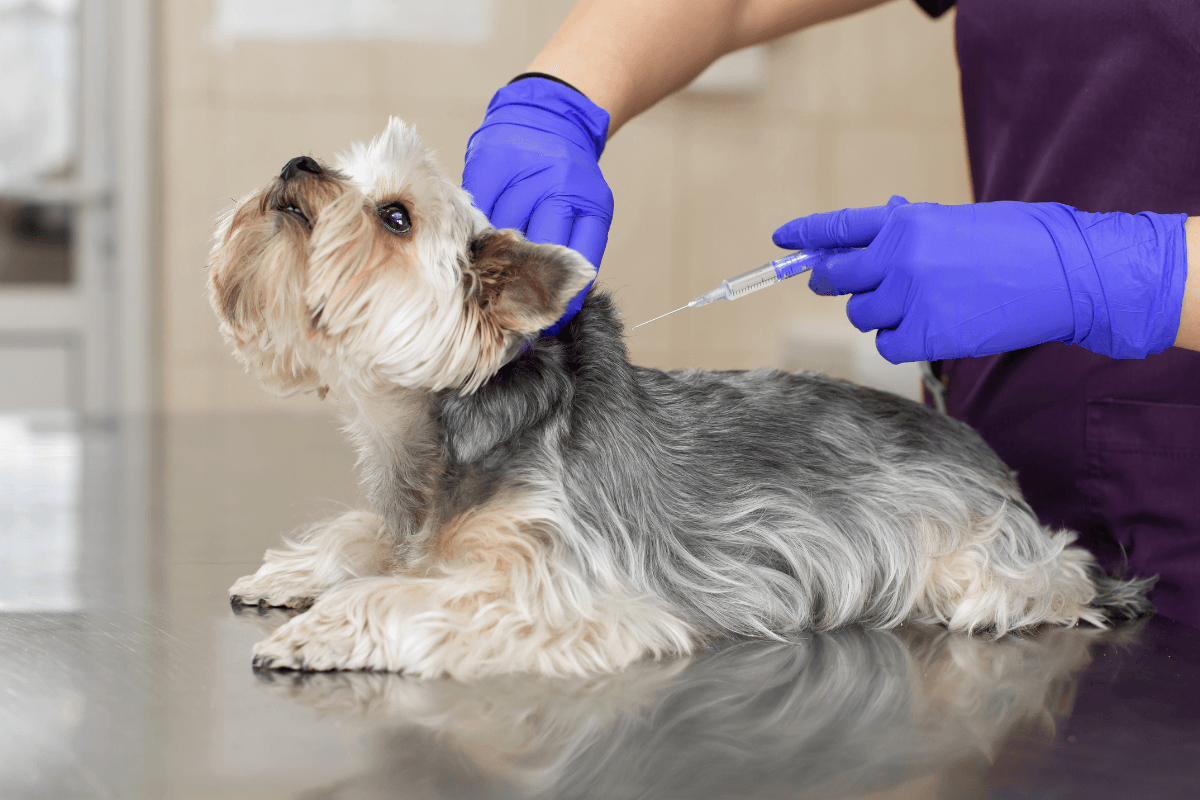
Giving Injections Safely at Home
Most pets accept insulin injections with calm, steady handling. Prepare supplies in a quiet spot and verify the insulin name, concentration (U‑40 or U‑100), and the correct matching syringe. Gently roll suspensions if indicated; do not shake unless the label specifies. Rotate sites, typically along the side of the chest or abdomen, to avoid irritation.
Learn how to give a dog an insulin shot from your veterinary team, then practice under supervision. When reading guides about insulin shots for dogs, focus on syringe alignment, tenting the skin, and slow, controlled delivery. For storage and appearance differences, What Is Cloudy Insulin clarifies why some products look milky. If you need a refresher on hormone function, Role Of Insulin offers a concise overview of how insulin affects metabolism.
Tip: Create a checklist: verify pet identity, insulin type, syringe scale, dose, and site rotation. Pause if anything seems off, and call your vet before proceeding.
Avoiding Hypo/Hyperglycemia Risks
Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can occur if your pet eats less, exercises more, or receives too much insulin. Early signs include hunger, restlessness, and weakness; severe cases may cause seizures. High blood sugar (hyperglycemia) may present as thirst, urination, and weight loss. Both require prompt veterinary guidance to prevent complications.
Know the symptoms of insulin overdose in dogs and keep emergency carbohydrates available if your vet approves. Ask your clinic for a written plan covering missed meals, vomit episodes, or unexpected exercise. For evidence‑based management frameworks, review the AAHA diabetes guidelines for dogs and cats, which outline monitoring and adjustment principles AAHA diabetes guidelines. If poor appetite or abdominal pain occurs, Pancreatitis In Cats describes a related condition relevant to feline stability.
Common Owner Questions on Amounts and Adjustments
Owners sometimes ask, “is 20 units of insulin a lot for a dog” after hearing numbers from others. Dose size alone does not indicate safety or control; what matters is response, trends, and veterinary direction. Dogs vary in insulin sensitivity, body weight, and concurrent disease, so comparisons rarely help. Call your clinic whenever intake, energy, or glucose readings shift unexpectedly.
It is also common to compare products or switch brands during shortages. Any change should be planned and monitored with your vet. For stepwise guidance on avoiding mistakes during transitions, How We Help Pet Owners describes process checks and documentation. If you want broader reading on endocrine basics, Diabetes Articles collects educational pieces that explain physiology and care.
Working With Your Veterinary Team and Next Steps
Diabetes care succeeds when owners, veterinarians, and nurses share timely information. Bring logs of feeding times, doses, behavior, and any home glucose values. Mark unusual events like missed meals or activity spikes. These details help your vet refine the plan safely and efficiently.
Ask how they define the maximum insulin dose for dogs within your clinic’s protocols, and what monitoring steps accompany any increase. Clarify when to perform a glucose curve at home versus in‑clinic. For labeled canine insulin instructions and safety notes, see Vetsulin prescribing information provided by the manufacturer Vetsulin prescribing information. For ongoing pet wellness content, explore Pet Health Articles to build confidence in daily routines.
Supplies, Storage, and Handling
Insulin is sensitive to heat and light. Store unopened vials as directed and keep opened products within label temperature ranges. Never freeze insulin, and avoid direct sunlight or hot cars. Track expiration dates and discard if the product looks abnormal or forms clumps not expected for that formulation.
Use the correct syringe scale for your insulin concentration, and never mix brands without veterinary guidance. Keep a backup vial and fresh needles if your vet recommends it. For product availability within endocrine care, Diabetes Products highlights related items for discussion with your veterinarian. If you notice persistent high readings despite correct use, discuss a curve or fructosamine before any changes.
Recap
Diabetes management blends the right insulin, careful technique, and steady monitoring. Keep routines consistent, record daily observations, and stay in close contact with your veterinary team. Small adjustments guided by data can improve stability and comfort for dogs and cats.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.