Knowing how to use glucagon injection kit can help reverse severe hypoglycemia when a person cannot safely swallow. This guide explains when to act, how to prepare the device, and the safest way to give an injection. It also covers aftercare, common errors, and newer alternatives.
Key Takeaways
- Recognize severe hypoglycemia fast; act before loss of consciousness.
- Check contents, clarity, and expiry before mixing the powder.
- Use proper injection sites and steady technique for safety.
- Call emergency services after dosing; monitor until fully alert.
- Train caregivers ahead of time and refresh skills regularly.
When to Act: Recognize Severe Hypoglycemia
Use glucagon when the person is unconscious, having a seizure, or unable to swallow safely due to low blood sugar. Classic signs include confusion, slurred speech, shaking, sweating, pallor, and sudden behavior changes. Rapid recognition matters because prolonged hypoglycemia can injure the brain and heart.
If convulsions appear, keep the person safe from injury and turn them on their side. For seizure features and safety steps, see Diabetic Seizures Symptoms for additional context. If fasting or missed meals trigger lows, the Fasting Hypoglycemia Guide offers background for prevention planning.
Prepare and Check the Kit
Before an emergency occurs, open the box and review every component. Confirm you have the vial with powder, the prefilled syringe or diluent, and the instructions. Store the device as directed and note the expiration month. When help is needed, you should only spend seconds checking the device, not reading it for the first time.
Check clarity and date during emergencies as well. Do not use if the powder appears discolored or the solution becomes cloudy after mixing. This is essential to ensure safe use and supports Glucagon Injection Kit With Diluent reference materials for device components and pack contents. To guide home storage routines, review manufacturer details on Diabetes Articles for storage thresholds and reminders.
Note: Regularly review glucagon storage and expiration with household members so the kit is ready.
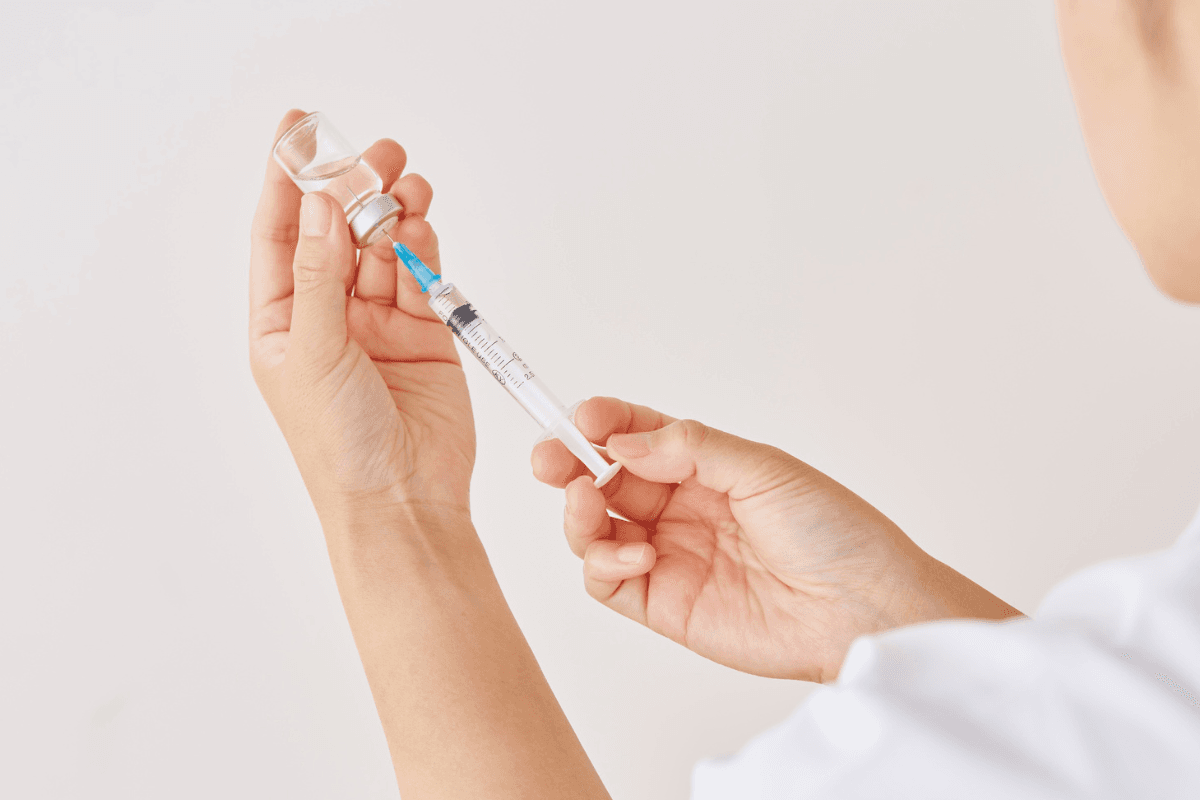
How to Use Glucagon Injection Kit: Step-by-Step
Call or have someone call local emergency services first. Place the person on their side to reduce the risk of aspiration. Remove the cap from the syringe or diluent and the cap from the vial. Insert the needle through the vial’s stopper and push all diluent into the powder.
Gently swirl the vial until the solution is clear. Draw up the prescribed dose from the vial, keeping the needle tip in the liquid to avoid drawing air. Choose an appropriate site, clean it if possible, and inject at 90 degrees into muscle or subcutaneous tissue. Hold steady, then withdraw the needle and apply light pressure with gauze.
Dosing, Sites, and Technique
Give the labeled dose per age and weight. Adults and adolescents typically receive 1 mg intramuscularly (IM) or subcutaneously (SC). Children under ~25 kg may receive 0.5 mg (consult the specific product label). These values reflect approved labeling and should not be adjusted without medical guidance. For official dosing language, see the FDA prescribing information, which explains standard indications and cautions.
Select sites with adequate tissue, such as the mid-thigh, upper arm (deltoid), or buttock. Insert the needle quickly, then press the plunger steadily. Hold the syringe still to prevent tissue injury. Needle handling basics also apply to insulin; for technique familiarity, see BD Ultrafine II Syringes for needle characteristics and handling concepts.
Injection Sites and Practical Positioning
Thigh injections are often easiest when the person is supine or on their side. Expose the site, and if time permits, clean with an alcohol swab. If clothing cannot be removed safely, inject through thin fabric; prioritize speed over sterility when life-threatening hypoglycemia is present. After injecting, massage is generally unnecessary. Maintain lateral positioning in case nausea or vomiting follows reversal. If the person remains unresponsive after 15 minutes, a second dose may be considered per label, while awaiting emergency responders.
Mixing and Reconstitution
Use gentle swirling only. Vigorous shaking can cause foaming and dosing errors. Mix until the solution is clear, not cloudy. If particulates remain or the color seems off, discard and use a backup device if available. Mixing correctly supports reliable absorption and effect.
In training sessions, practice with a demo device or expired vial so steps feel natural. Reviewing manufacturer videos helps cement proper technique. If you need a refresher on dilution steps, focus specifically on glucagon mixing and reconstitution to avoid underdosing. For device familiarity, the product page for Glucagon Injection Kit With Diluent can help identify the vial and diluent parts at a glance.
Special Situations: Children and Older Adults
Caregivers should learn how to give glucagon to a child using weight-appropriate dosing and calm, simple language. Stabilize the child on their side before injecting. Children may cry or move; recruit a second adult to steady the limb if possible. After recovery, offer small, frequent carbohydrates to reduce rebound lows.
Older adults may have frailty or bruising risk. Choose sites with adequate tissue and avoid areas with skin tears. Monitor closely for nausea and blood pressure shifts. For families managing type 1 diabetes, explore Type 1 Diabetes Articles to support caregiver training and routine planning.
Aftercare and Monitoring
Once the person awakens and can swallow safely, give fast-acting carbohydrates, followed by a snack with carbohydrate and protein. Examples include glucose tablets or gel. For practical options to restock your kit, see Dextrose for fast glucose sources that act quickly. Continue checking glucose at regular intervals for several hours to catch recurrent lows.
Contact the care team to review the trigger and adjust prevention plans. If the low followed new medication or alcohol intake, discuss risk reduction steps. For easy post-event glucose checks, the Freestyle Freedom Lite Meter overview explains practical home monitoring tips. Keep notes about timing, dose, and recovery to refine your hypoglycemia action plan.
Alternatives and Newer Devices
Nasal and auto-injector options can simplify delivery. If you prefer needle-free delivery, learn how to use Baqsimi nasal glucagon from manufacturer instructions. For official device use and safety information, see the Baqsimi prescribing information. Some users favor prefilled auto-injectors for a simpler workflow during stressful events.
Training should match the device you carry. For those considering nasal formulations, review Baqsimi Nasal Powder to compare features and pack contents. If you or your caregiver prefer pen-style delivery, discuss availability of auto-injector options with your clinician; manufacturer resources also explain step-by-step handling.
Training, Delegation, and Storage
Anyone close to a person at risk should be trained: family, roommates, coworkers, school staff, and sports coaches. Many kits include trainer devices or simple checklists. Quick, hands-on practice reduces hesitation during emergencies. The American Diabetes Association advises that at-risk individuals have ready-to-use glucagon, and that caregivers know how to administer it; see the ADA Standards of Care for professional guidance supporting preparedness.
Store kits at the recommended temperature and away from light. Replace them before expiry and after any use. Create calendar reminders, and keep a visible note in diabetes supplies. For broader diabetes self-management topics, browse Diabetes Articles to reinforce daily routines that prevent severe lows.
Safety: Side Effects and Contraindications
Common reactions include nausea, vomiting, headache, and transient blood pressure or heart rate changes. These usually resolve quickly as glucose normalizes. Severe reactions are uncommon but warrant medical evaluation. People with certain rare tumors, such as pheochromocytoma or insulinoma, have specific risks and should use glucagon only under medical guidance; consult the product label for details.
Glucagon can raise blood glucose and increase catecholamine release. Use caution with conditions affected by these responses. For precise contraindications and special populations, the FDA prescribing information provides authoritative safety listings. If persistent vomiting follows dosing, continue lateral positioning to lower aspiration risk while awaiting responders.
Common Errors and Prevention
Most errors occur under stress. To reduce mistakes, rehearse your steps quarterly. Keep instructions inside the kit and label the box with a bold reminder to call emergency services first. Avoid partial mixing, injecting air, or using expired supplies. If two caregivers are present, assign roles: caller, preparer, injector, and timer.
Typical pitfalls include skipping reconstitution, uncertainty about dose, and missed injection sites. A brief checklist on the box can help. To reduce mix-ups, practice with a trainer and review glucagon preparation errors to avoid during routine diabetes education sessions. For broader technique skills that translate across injections, see Ways of Administering Insulin for general injection principles and setup habits.
Recap
Severe hypoglycemia is a medical emergency. Preparedness, clear steps, and calm technique improve outcomes. Review your kit, refresh training, and make sure nearby adults can act. After any event, debrief with the care team and update your action plan accordingly.
Tip: Keep one kit at home and another in a bag that always travels with the person.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.