Please note: a valid prescription is required for all prescription medication.
Baqsimi Nasal Powder Product Overview and Safety
Start 2026 with savings: Use code SAVE10 for 10% OFF all RX meds. Jan–1 Mar. Ozempic from Canada and Mounjaro Vial not included. Offer valid until March 1st. Coupon code cannot be combined with other offers. For products with “Bulk Savings”, the discount will be applied to the regular price for 1 unit. Maximum allowable quantity equal to a 90 day supply per single order.
$179.99
You save


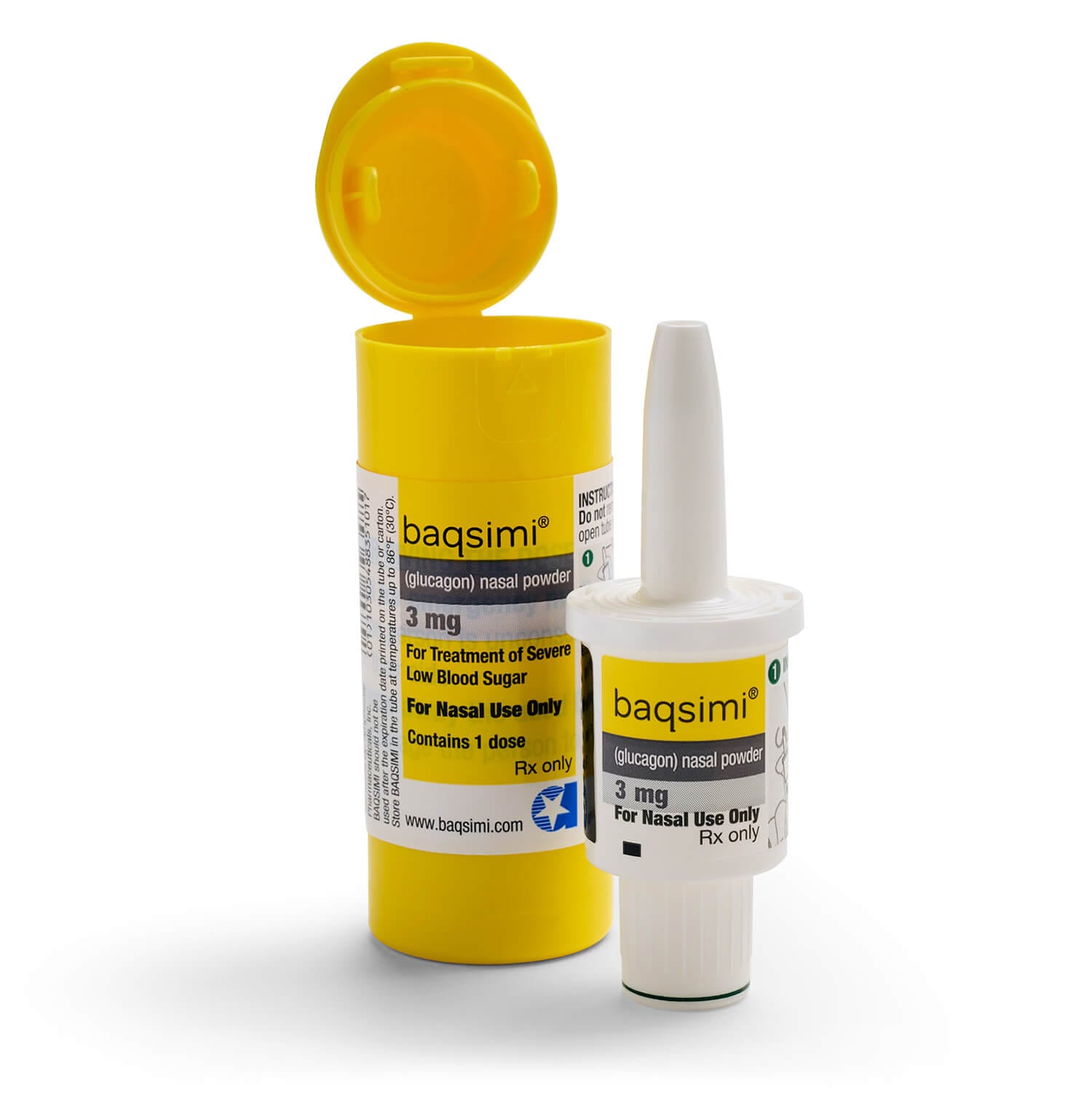
Baqsimi is a single-use nasal glucagon medicine used for severe low blood sugar emergencies. Baqsimi Nasal Powder is designed to be given quickly when a person with diabetes cannot safely take sugar by mouth. This page summarizes how it works, practical use basics, and key safety points to review with a clinician.
It is not a daily diabetes medicine, and it does not replace routine glucose monitoring or meal planning.
What Baqsimi Nasal Powder Is and How It Works
This medicine contains glucagon, a hormone that raises blood glucose by signaling the liver to release stored sugar (glycogen) into the bloodstream. CanadianInsulin acts as a prescription referral service and may confirm details with prescribers. Some patients explore US delivery from Canada when building an emergency hypoglycemia plan, depending on eligibility and jurisdiction.
Because it is given into the nose, the person does not need to swallow or drink during the episode. The medicine can be used even if the person is unconscious, but follow the prescribing information and local emergency guidance. Where permitted, licensed third-party pharmacies dispense and prepare the medication for patient use. After the person wakes and can swallow, a fast source of carbohydrate and a longer-acting snack are commonly used to help prevent the low from returning, based on a clinician’s plan.
Who It’s For
Baqsimi is intended for treatment of severe hypoglycemia (very low blood glucose) in people with diabetes. In practical terms, this can include situations where the person is confused, having a seizure, unconscious, or unable to take oral carbohydrate safely. It is typically prescribed in advance so caregivers, family members, coworkers, or school staff can respond during an emergency.
This treatment is not for routine, mild lows that can be managed with food or glucose tablets. A clinician will also review whether glucagon is appropriate if the person has rare conditions such as insulinoma (an insulin-producing tumor) or pheochromocytoma (an adrenal tumor), where glucagon may cause harmful effects. Anyone with a known allergy to glucagon or product ingredients should not use it.
Dosage and Usage
The device is designed to deliver a single dose into one nostril. The person does not need to inhale; the dose is delivered when the plunger is pressed. Baqsimi Nasal Powder is generally taught as an emergency medicine that a bystander can give while contacting emergency services, then placing the person on their side if vomiting occurs. If the person does not respond, the prescribing information describes when an additional dose may be used if available while continuing to seek urgent help.
Why it matters: Training a few helpers ahead of time can reduce delays during a true emergency.
Training and emergency planning
Ask the prescriber or diabetes educator for hands-on teaching and written steps that fit the person’s usual regimen. Planning often includes when to use glucagon versus oral carbohydrate, who should be called, and what information to share with responders. It can also help to document where the device is stored at home, work, school, and during travel. For broader context on diabetes treatment approaches, the guide Common Diabetes Medications can help explain how different medicines affect blood glucose. If home monitoring is part of the routine, Check Sugar Level outlines practical measurement basics and common sources of error.
Strengths and Forms
This product is supplied as a preloaded, single-use intranasal device containing one measured dose of glucagon nasal powder. The commonly referenced presentation is a 3 mg dose; packaging configuration can vary by pharmacy, region, and current supply. Because it is a one-time device, a new unit is used for each separate episode.
The table below summarizes key form factors that matter for preparedness rather than day-to-day dosing.
| Feature | What to know |
|---|---|
| Route | Intranasal (into the nostril) |
| Device type | Single-use, premeasured |
| Typical role | Rescue treatment for severe hypoglycemia |
| Refills | Replace after use or expiration |
Storage and Travel Basics
Store the device according to the label, typically at controlled room temperature, and keep it in its original packaging to protect it from moisture. Avoid using it after the expiration date, and consider setting reminders to check dates a few times per year. If the outer packaging looks damaged or wet, ask a pharmacist whether replacement is needed.
Quick tip: Keep one device in a consistent, labeled location that caregivers can find.
For travel, carry rescue medicine in a bag that stays with the person rather than in checked luggage. Extreme heat can be a risk in parked cars, beach bags, and glove compartments. If diabetes-related gear is part of the trip, the overview Diabetes Devices may help with organizing meters, sensors, and backup supplies. People who experience lows more often should review prevention strategies with a clinician and use a personalized plan.
Side Effects and Safety
Common side effects with nasal glucagon can include nausea, vomiting, headache, and temporary nose or throat irritation such as watery eyes, congestion, or discomfort. These effects can overlap with symptoms after a severe low itself, so it can help to monitor how the person feels as they recover. If vomiting occurs, turning the person onto their side can reduce choking risk until they are fully alert.
Serious reactions are uncommon but can occur. Seek urgent care for signs of a severe allergic reaction such as trouble breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or widespread rash. People with certain tumors, including pheochromocytoma, may have a dangerous rise in blood pressure with glucagon, and those with insulinoma may have worsening hypoglycemia afterward. A prescriber can help weigh risks and discuss what to do after administration, including when emergency services should be involved.
Drug Interactions and Cautions
Some medicines can change how the body responds to glucagon or how the heart reacts during recovery. For example, beta-blockers may increase the likelihood of a faster heartbeat or higher blood pressure after glucagon. Certain anti-inflammatory medicines such as indomethacin have been reported to reduce the blood-glucose response to glucagon, and anticoagulants like warfarin may have altered effects; a clinician can advise on relevance for an individual.
Alcohol use, prolonged fasting, adrenal insufficiency, and severe malnutrition can reduce liver glycogen stores, which may limit how well glucagon raises glucose. This is one reason emergency follow-up matters even if the person wakes quickly. For related background on balancing insulin, meals, and activity, see Basal Vs Bolus and the diabetes hub Diabetes Condition for browseable lists of common therapies.
Compare With Alternatives
Rescue options for severe hypoglycemia generally fall into a few categories. Injectable glucagon kits are an established alternative, but they may require mixing before injection and can be harder for untrained helpers during a crisis. For an example of this format, see Glucagon Injection Kit. Intravenous dextrose is another option used by healthcare professionals in clinical settings, especially when rapid access is needed.
For mild or early lows, oral carbohydrates (such as glucose tablets, gel, or juice) are often sufficient when the person is awake and able to swallow safely. Baqsimi Nasal Powder differs in that it is intended for situations where swallowing is unsafe or the person is not fully responsive. Deciding what to keep on hand often depends on hypoglycemia history, who is available to help, and how quickly the person tends to recover.
Pricing and Access
Access depends on prescription status, local rules, and whether coverage is available through a private plan, employer benefits, or public programs. Some people also consider cash-pay options, including scenarios without insurance, but out-of-pocket totals can vary based on pharmacy pricing, strength, and pack configuration. Documentation needs typically include a valid prescription and basic patient identifiers, and pharmacies may need to clarify directions or prescriber information before processing.
CanadianInsulin helps coordinate prescription referrals, and prescription details may be verified with the prescriber before release. Cross-border fulfilment may be considered when allowed by jurisdiction and patient eligibility. For general site context and updates that may affect availability, Promotions Information is a neutral reference point, but any coverage decision should be confirmed directly with the payer.
If a household relies on rescue glucagon, it can help to keep more than one unit in different locations and to replace devices before they expire. Some patients also browse diabetes-related items in hubs like Diabetes Category and Hypoglycemia Aids to compare formats and storage needs. Education resources in Diabetes Articles, including Staying Healthy While Sick, can also support prevention planning around illness-related glucose swings.
Authoritative Sources
For FDA-reviewed prescribing details and warnings, refer to the FDA label for glucagon nasal powder.
For patient-focused education on low blood glucose recognition and response, see the American Diabetes Association overview of hypoglycemia.
When a pharmacy ships temperature-sensitive medicines, it may use prompt, express, cold-chain shipping to help maintain stability.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Express Shipping - from $25.00
Shipping with this method takes 3-5 days
Prices:
- Dry-Packed Products $25.00
- Cold-Packed Products $35.00
Standard Shipping - $15.00
Shipping with this method takes 5-10 days
Prices:
- Dry-Packed Products $15.00
- Not available for Cold-Packed products
What is Baqsimi used for?
Baqsimi is a rescue medicine used to treat severe hypoglycemia (very low blood glucose) in people with diabetes. It is intended for emergencies when the person cannot safely take sugar by mouth, such as when they are unconscious, having a seizure, or too confused to swallow. It is not a daily diabetes medication and is not meant to replace routine monitoring, meal planning, or adjustments to insulin or other therapies. The prescribing information and a clinician’s instructions should guide when it is appropriate to use.
How do you give glucagon nasal powder during an emergency?
Glucagon nasal powder is supplied in a single-use device that is placed into one nostril and activated by pressing the plunger. The person does not need to inhale for the dose to be delivered. Because this is an emergency situation, many care plans include contacting emergency services right away and monitoring breathing and responsiveness while waiting for help. After the person wakes and can swallow safely, a clinician may recommend oral carbohydrate to reduce the chance of another low.
Can Baqsimi work if someone has a cold or nasal congestion?
Nasal symptoms such as congestion or a runny nose can happen in everyday life, and people often wonder whether they affect intranasal glucagon. Baqsimi is designed to be absorbed through the nasal lining, and it is still intended for use in severe hypoglycemia even if the person is not able to inhale normally. That said, individual response can vary, and the official prescribing information is the best source for details. Ask a clinician how illness might affect your overall hypoglycemia plan.
What side effects should caregivers watch for after giving Baqsimi?
Common side effects can include nausea, vomiting, headache, and temporary nose or throat irritation (watery eyes, discomfort, congestion). Because vomiting can occur, it is important to protect the airway and place the person on their side if they are not fully alert. Get urgent medical help for signs of a severe allergic reaction such as trouble breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or widespread rash. Follow-up is also important because severe hypoglycemia can recur, especially if the underlying cause is not corrected.
When should emergency services be called after giving rescue glucagon?
Severe hypoglycemia is a medical emergency, and many action plans include calling emergency services at the time glucagon is given, especially if the person is unconscious, having a seizure, injured, pregnant, or not improving promptly. Even if the person wakes up, medical evaluation may be appropriate because the low can return and the cause may need treatment. Local guidance and the prescribing information should be followed, and caregivers should use the patient’s clinician-provided emergency instructions when available.
What should I ask the clinician when getting a Baqsimi prescription?
Helpful questions include: who should be trained to administer it, when to use glucagon versus oral glucose, and what steps to take immediately afterward. Ask about whether a second dose could be needed and how that should fit into your emergency plan. It is also reasonable to review medical conditions and medicines that may change safety, such as beta-blockers, adrenal problems, or rare tumors like insulinoma or pheochromocytoma. Finally, confirm storage instructions, expiration checks, and where to keep devices at home and away.
Rewards Program
Earn points on birthdays, product orders, reviews, friend referrals, and more! Enjoy your medication at unparalleled discounts while reaping rewards for every step you take with us.
You can read more about rewards here.
POINT VALUE
How to earn points
- 1Create an account and start earning.
- 2Earn points every time you shop or perform certain actions.
- 3Redeem points for exclusive discounts.
You Might Also Like
Related Articles
Zepbound Pill Clarified: Injection Reality and Oral Research
Key Takeaways Current form: Zepbound is an injectable medicine, not a tablet. Search intent: “pill” usually means convenience, not a new product. Dosing language: labels use stepwise titration and maintenance…
Lancets For Blood Sugar Testing: Selection And Safety Tips
OverviewFingerstick blood glucose checks rely on small, sharp tools and consistent technique. In most home setups, a spring-loaded lancing device uses lancets to puncture skin and produce a drop of…
SGLT2 Inhibitors Explained: Uses, Risks, and Examples
Key Takeaways These medicines lower blood sugar by acting in the kidneys. Some are also labeled for heart failure or chronic kidney disease. Drug names include dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, and canagliflozin.…
Out Of Pocket Cost For GLP-1 Medications: Planning Tips
Key Takeaways Costs vary by drug, indication, and dose form Cash-pay totals include more than the pen Programs exist, but eligibility is limited Be cautious with compounded versions and unverifiable…