For people managing type 2 diabetes, understanding what is bydureon can help frame options for weekly GLP-1 therapy. This overview explains mechanism, devices, dosing basics, safety, and availability. It also outlines alternatives and practical next steps if supply changes or treatment goals shift.
Key Takeaways
- Weekly GLP-1 option: supports glucose control and modest weight effects.
- Device formats vary: pen and BCise autoinjector existed in different markets.
- Availability changes: supply and status differ by region and time.
- Common reactions: nausea and injection-site nodules may occur.
- Plan transitions: discuss alternatives and switching protocols with your clinician.
What Is Bydureon?
Bydureon is the extended-release form of exenatide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA). It delivers medicine once weekly to help lower blood glucose in adults with type 2 diabetes, alongside diet and activity. It is not insulin and does not replace metformin or other core oral agents, but it can be combined with them when clinically appropriate.
Historically, Bydureon was supplied as a reconstitution kit, a premixed pen, and the BCise autoinjector in some regions. The brand’s exact devices and names—such as bydureon bcise—varied by market and time. Because device availability impacts technique and training, always confirm the specific device and instructions you receive.
Is Bydureon a GLP-1 and How Does It Work?
Mechanistically, is bydureon a glp-1 therapy? Yes. Exenatide activates GLP-1 receptors to enhance glucose-dependent insulin secretion, reduce glucagon after meals, slow gastric emptying, and help reduce appetite. These actions can improve A1C and fasting glucose, especially when combined with nutrition and activity programs.
Clinical guidance places GLP-1 RAs among preferred non-insulin options for type 2 diabetes, especially when weight management or low hypoglycemia risk is important. For a broader overview of this class and where exenatide fits, see GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for class benefits and limitations. You can also explore the Type 2 Diabetes hub for context on treatment algorithms.
Regulators approved exenatide extended-release as adjunctive therapy to diet and exercise in adults with type 2 diabetes. For labeled indications, boxed warnings, and contraindications, review the FDA prescribing information, which outlines class-specific risks and use limitations.
Forms, Devices, and Availability
Bydureon historically came as a premixed pen, a reconstitution kit, and the BCise autoinjector. The bydureon pen required mixing in some versions, while the BCise device simplified preparation by using a prefilled chamber. The BCise presentation was commonly described as a 2 mg weekly injection, and many users appreciated the simpler handling compared with earlier kits. In practice, your exact device matters because technique and readiness steps differ.
Device and market status have evolved in recent years. Supply constraints and market withdrawals have been reported, and regional listings may change. If you are wondering is bydureon bcise still available, check local pharmacy channels or your clinician’s guidance for current status. For background on the exenatide brand’s device history, see the Bydureon Exenatide Guide, which summarizes presentations and clinical use over time.
Dosing, Timing, and Injection Technique
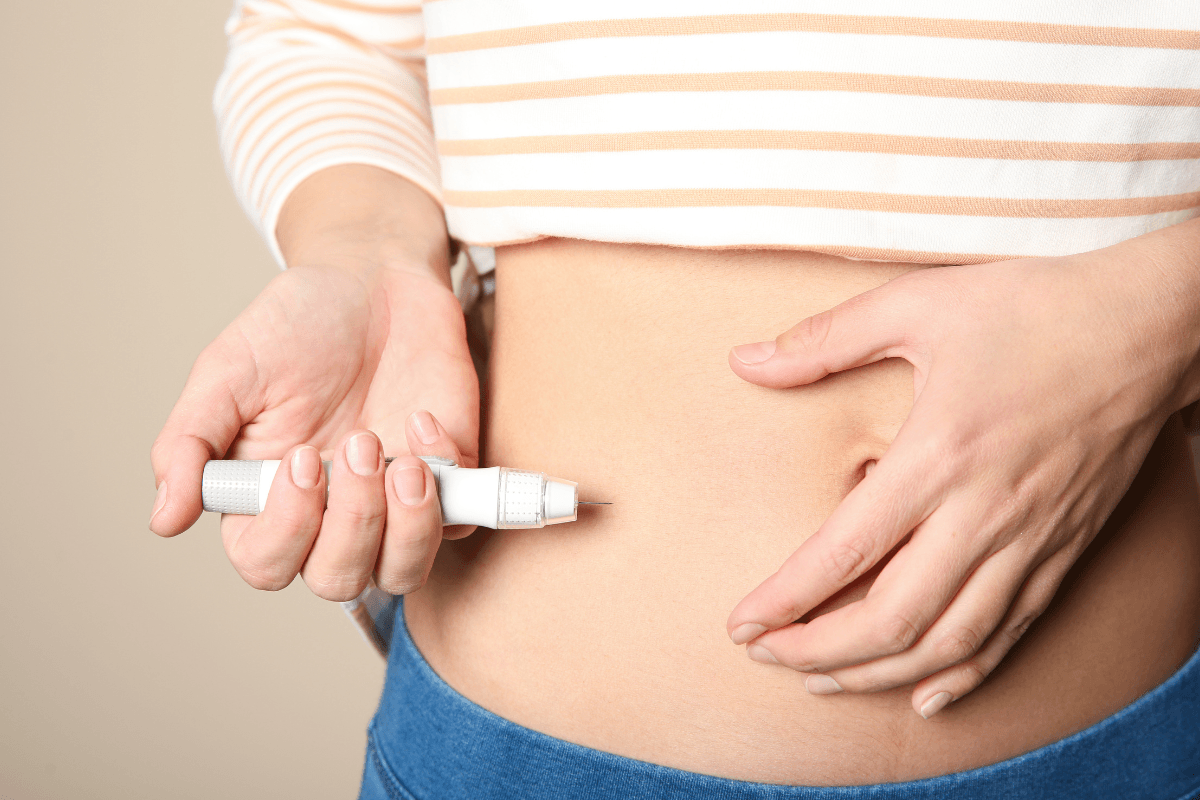
Bydureon is administered once weekly on the same day each week. Choose a time you can remember consistently. You may inject into the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm, rotating sites to reduce local reactions. If your regimen includes other injections, separate sites to avoid overlapping irritation. Always confirm your device’s preparation steps before use.
Many users ask about bydureon injection how to give. With the BCise autoinjector, you typically warm the device to room temperature, mix as directed, then press and hold to deliver the dose until the indicator confirms completion. With pen or kit formats, follow the supplied mixing and needle attachment steps carefully. For general injection technique context across non-insulin injectables, see Injectable Alternatives for Type 2, which discusses handling rhythms and site rotation. For needle gauge and handling basics, the BD Ultrafine II Syringes page outlines common sizes used with injectable therapies.
Tip: Build a weekly reminder system and a rotation map. This simple routine lowers the chance of missed doses and reduces localized skin irritation.
Side Effects, Warnings, and Interactions
Common effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, decreased appetite, and injection-site reactions. With exenatide extended-release, small, firm nodules at the injection site are relatively frequent and usually resolve over weeks. Headache, fatigue, and indigestion can occur as the body adapts. Report persistent or severe symptoms to your clinician, especially if hydration or nutrition are affected.
Serious risks are uncommon but important. The class label includes a boxed warning regarding thyroid C-cell tumors observed in rodents, and the medicine should not be used in patients with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or MEN 2. Pancreatitis and gallbladder issues have been reported with GLP-1 RAs. For a focused discussion, see Bydureon Side Effects for symptom patterns and when to seek care. For full risk language and contraindications, review the FDA prescribing information. Patients sometimes search for bydureon bcise side effects because device-specific instructions can influence injection-site experiences.
Weight Effects: What to Expect
Many patients are interested in bydureon weight loss. GLP-1 RAs can reduce appetite and promote modest weight reduction in people with type 2 diabetes, though individual responses vary. Exenatide’s weight effects are typically smaller than those seen with more potent agents in this class. Weight change also depends on nutrition planning, physical activity, and co-prescribed medications that may increase appetite.
Bydureon for weight loss in non diabetics is not an approved use. When weight is the primary goal, consider whether a GLP-1 or dual-agonist approved for obesity would be more appropriate. For outcomes and expectations, see Bydureon Weight Loss for evidence summaries. To compare weight-focused agents, the Best GLP-1 for Weight Loss guide reviews newer options and their differences.
Comparisons, Alternatives, and Transitions
Bydureon and semaglutide are not the same medicine, and dosing strength, device, and potency differ. When patients consider a switch, evidence and goals should guide the decision. Clinicians often compare GLP-1 options on A1C reduction, weight impact, and tolerability. For side-by-side details, see Ozempic vs Bydureon for comparative efficacy and device differences and Trulicity vs Bydureon for weekly-by-weekly alternatives.
When supply changes or goals shift, switching from bydureon to ozempic may be considered. Transitions should account for dose equivalence, timing of the last weekly dose, and gastrointestinal tolerability. Do not co-administer overlapping GLP-1 RAs. If seeking broader perspective on incretin choices, Bydureon vs Victoza highlights daily versus weekly trade-offs. Class education within GLP-1 Receptor Agonists can help set reasonable expectations about benefits and limitations.
BCise, Pens, and Practical Device Notes
The BCise autoinjector was designed for fewer steps and concealed-needle administration. Many users refer to it as the bydureon bcise pen, though its mechanics differ from a classic pen. The BYDUREON BCise 2 mg autoinjector allowed a single weekly activation after mixing. In contrast, a traditional bydureon pen may require different preparation and needle attachment. Because device steps influence reliability, ask your pharmacist to demonstrate the exact device you receive.
Availability has shifted over time, with reports of bydureon bcise availability fluctuating due to regional supply or portfolio changes. Patients also search for bydureon bcise discontinued or bcise shortage when pharmacies cannot fill requests. If access is limited, discuss a temporary alternative in the same class or a different mechanism entirely. That conversation should include coverage, titration needs, and anticipated side effects with the new option.
Note: Manufacturer branding and market listings change. AstraZeneca has been the primary bydureon manufacturer; local distribution, however, depends on regional approvals and policies.
Everyday Use: Tips, Missed Doses, and Food Interactions
Consistency matters with weekly injections. If you miss a dose, many labels allow administration when remembered if the next dose is not imminent; otherwise, skip and resume on your usual day. Because exenatide can slow gastric emptying, be mindful with medications that require rapid absorption. Separate timing if directed by your prescriber.
To reduce gastrointestinal symptoms, some people take the dose on an evening routine and keep meals smaller during the first weeks. If nausea persists or worsens, ask your clinician about adjustments elsewhere in your regimen. For broader injectable context and site-rotation strategies, see Injectable Alternatives for Type 2, which includes practical handling advice across non-insulin agents.
Recap
Bydureon is a once-weekly exenatide therapy that helps lower glucose and may support modest weight change. Device formats have included BCise and pen-based systems, though availability has evolved by market. Safety focuses on gastrointestinal effects, injection-site nodules, and class warnings. If access is limited or goals change, work with your clinician on alternatives and a safe transition plan.
For readers comparing options, start with class context in GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and then review matchups like Ozempic vs Bydureon based on your priorities.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.