Key Takeaways
- Higher risk profile: Diabetes raises infection risk and slows healing.
- Red flags matter: Fever, rapid spread, or severe pain need urgent care.
- Treat sources: Manage skin breaks, tinea pedis, and edema to prevent relapse.
- Track progress: Outline the area, monitor glucose, and reassess at 48–72 hours.
The overlap of cellulitis and diabetes demands careful attention. This infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue can progress faster and heal slower when blood glucose runs high. Understanding early warning signs, safe home measures, and when to seek medical care helps reduce complications and repeat infections.
Cellulitis and Diabetes: When to Worry
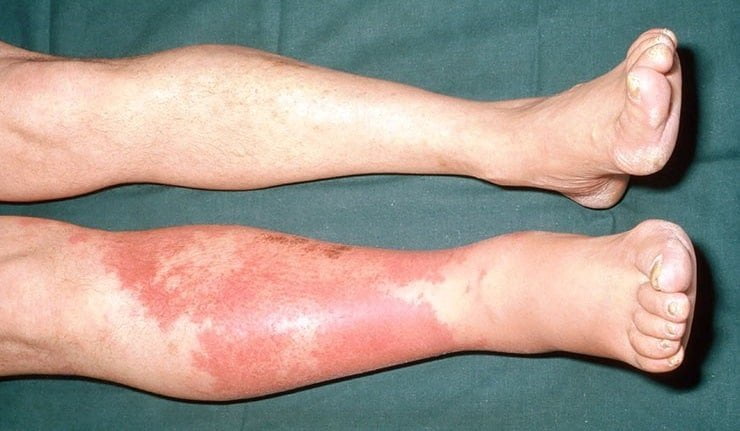
Start by recognizing typical features. The affected area looks red, warm, swollen, and tender. Skin may feel tight and painful, and movement can worsen discomfort. Some people notice a low-grade fever or chills. In diabetes, neuropathy (reduced sensation) can blunt pain, so visual checks become more important.
Know the escalation cues. Seek urgent care for severe pain out of proportion, spreading redness over hours, rapidly increasing swelling, or new numbness. Go to the emergency department with high fever, shaking chills, vomiting, confusion, or lightheadedness. Wound drainage with foul odor, black or dusky skin, or crepitus (a crackling feel) also warrants immediate evaluation, as these signs can indicate deeper infection.
For evidence-based clinical criteria on serious skin infections, the Infectious Diseases Society of America offers detailed practice guidelines that clinicians use to triage and treat patients.
What Cellulitis Looks Like and How It Spreads
Appearance varies by location and skin tone. On lighter skin, redness may look bright pink to crimson; on darker skin, look for warmth, swelling, and a shiny, tight surface. Edges are often indistinct, and the skin may pit with pressure. Lymphangitic streaks (thin red lines) can point toward deeper spread along lymph vessels.
Because many patients search for pictures of cellulitis, it helps to know key visual clues: asymmetric patches, warmth on touch, and tenderness with pressure. On the feet, fissures between toes or macerated skin from moisture often mark the entry point. On the face, look for swelling around the eyelids or cheeks and pain with chewing or eye movement. Arms can become involved after minor cuts, dermatitis, or IV lines.
Leg, Foot, and Face Patterns
Leg involvement is common in diabetes due to edema, venous disease, and unnoticed trauma. Patches may ring old scratches, insect bites, or small ulcers. Feet are vulnerable when neuropathy, calluses, or athlete’s foot weaken the barrier. Facial involvement can follow sinus infections, dental issues, or shaving cuts, and swelling may advance quickly.
Subtle early changes matter. Compare both limbs for asymmetry, mark the borders with a pen, and recheck in several hours. If the marked edge keeps widening, or pain intensifies despite rest and elevation, reassess promptly. For skin-condition overviews relevant to these patterns, see the Dermatology category for broader skin barrier discussions.
Why People With Diabetes Are at Higher Risk
The reasons are multifactorial. High glucose can impair neutrophil function (the white cells that fight bacteria) and reduce blood flow in small vessels. Neuropathy reduces protective sensation, so small injuries go unnoticed and untreated. Edema stretches the skin and makes it easier for bacteria to slip through micro-cracks.
When you ask why does diabetes cause cellulitis, consider the gateways that let bacteria in: eczema flares, interdigital fungal infections, ingrown toenails, and dry heel fissures. Each breach raises risk, especially when circulation is limited by peripheral artery disease. For prevention and foot self-care principles in diabetes, the American Diabetes Association’s foot care recommendations outline daily checks and protective habits.
Complications and Sepsis Risk
Most cases stay superficial, but some progress. Cellulitis sepsis symptoms include high fever, fast heart rate, rapid breathing, low blood pressure, confusion, or extreme sleepiness. Red streaks, tender lymph nodes, and sudden worsening swelling are additional danger signs. These patterns can indicate bacteria entering the bloodstream or spreading to deeper tissues.
Deep infections may involve abscesses, muscle, or bone (osteomyelitis). Hardware or prosthetic joints near the infection increase risk. If your blood sugars climb or remain unstable during illness, dehydration and immune stress can further complicate recovery. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provides a practical CDC cellulitis overview that summarizes symptoms and general risks.
Getting a Diagnosis and Useful Tests
Clinicians diagnose cellulitis by history and exam. They assess the site, warmth, tenderness, and any source such as ulcers or tinea pedis (athlete’s foot). They look for fluctuance (a soft, fluid feel) that may suggest an abscess. A pen outline helps track progression and informs treatment response at follow-up.
Tests depend on severity. Labs such as complete blood count, C-reactive protein, or blood cultures may be considered with systemic signs. Ultrasound can detect abscesses, while X-ray or MRI helps evaluate bone involvement if deep infection is suspected near chronic ulcers. If ulcers are present, swabs are less useful than debridement with culture from viable tissue.
For ulcer staging and care basics that intersect with infection assessment, see Diabetic Foot Ulcer for context on wound depth and tissue quality.
Treatment Strategy and Antibiotics
Clinicians tailor antibiotics to severity, likely organisms, and local resistance. Mild cases without systemic signs may begin with oral agents targeting streptococci and staphylococci. Risk factors for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) can prompt different choices. Moderate to severe cases, rapid progression, or facial involvement often need parenteral therapy and closer monitoring.
In the context of diabetic foot cellulitis treatment, care often includes debridement of devitalized tissue, pressure offloading, edema management, and strict glucose monitoring. Address portals of entry such as interdigital maceration or fissures. For broader skin and soft-tissue infection guidance, consult the Infectious Disease category for discussions on organism coverage and escalation principles.
Preventing recurrence requires treating fungal skin disease between the toes. For tinea pedis references that reduce skin breakdown risk, see Terbinafine for drug-class context and Ketoconazole for azole-based comparisons, as antifungals can help restore the skin barrier.
Recovery, Monitoring, and What If It’s Not Improving
Outline the involved area and recheck the edge after rest, elevation, and antibiotics. Some swelling may persist even as infection slows. Track body temperature and hydration. Keep glucose targets individualized and monitor more frequently, as acute illness can raise levels and hinder healing.
If cellulitis still red after antibiotics, consider several explanations. Inflammation can lag behind bacterial clearance, especially with lymphedema or venous disease. Alternatively, an abscess, resistant organisms, or an unaddressed source such as tinea pedis can drive persistence. Re-evaluation may involve imaging, changing antibiotics, or procedural drainage when indicated. For skin conditions that complicate recovery, the Dermatology library provides context on barrier repair and dermatitis control.
Prevention and Foot Care Checklist
Prevention starts with routine. Inspect feet daily, including between toes and heels. Moisturize dry skin but keep interdigital spaces dry. Trim nails straight across and seek help for thick or deformed nails. Wear well-fitting shoes and socks; avoid walking barefoot, even indoors. Manage edema with elevation, compression when recommended, and active movement.
Understanding what causes cellulitis in the legs guides prevention. Common drivers include athlete’s foot, dry skin fissures, minor trauma, and skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis. Treat tinea pedis promptly; antifungals reduce the constant microbreaks that invite bacteria. For antifungal options and ingredient differences, review Terbinafine comparisons and consult Infectious Disease for medication class overviews that relate to skin infections.
For wound risk grading details, see Diabetic Foot Ulcers to connect ulcer depth with infection risk. If you need a concise refresher on prevention basics, the Diabetes section offers related metabolic and foot-care coverage across conditions.
When to Seek Specialist Care and Coding Notes
Consider referral when infections recur, the limb has significant edema, or osteomyelitis is suspected. Podiatry can help with offloading, nail problems, and biomechanical issues. Infectious disease specialists advise on complex antibiotic choices and durations. Vascular evaluation matters if pulses are weak or wounds heal slowly. Coordinated care reduces relapse and preserves mobility.
Documentation supports continuity and benefits health systems. If you see references to diabetes with cellulitis icd-10, remember coding is context-dependent and typically handled by clinicians or medical coders. Notes should capture severity, systemic involvement, and any procedures performed. For a practical overview of skin infections that often require specialist input, see Infectious Disease for cross-linked topics on escalation pathways.
Recap
Diabetes changes the trajectory of skin infections by impairing barriers and slowing immune response. Early recognition, source control, and tailored antibiotics improve outcomes. Daily skin care and foot protection help prevent recurrences. When signs escalate or progress stalls, timely reassessment limits complications. For more depth on ulcers that often coexist with infection, review Diabetic Foot Ulcer to connect wound care with infection prevention.
Note: For consumer-friendly summaries of symptoms and risk, CDC resources provide helpful overviews, while IDSA guidelines outline clinician decision points across severities.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.