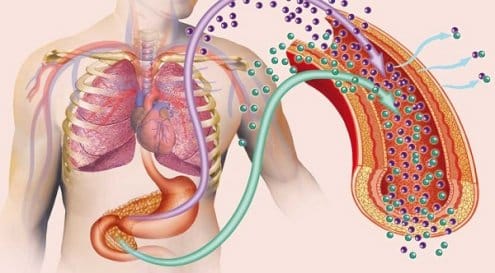
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body’s cells fail to absorb glucose from the blood properly, resulting in increased blood sugar levels. The cause of this disorder is insulin resistance, which is explored below.
Causes of Insulin Resistance
The exact cause of insulin resistance is not known, but extensive scientific research and clinical studies have established the following reasons as possible causes:
- Imbalance in calories due to a change in lifestyle, toxic foods, and/or a high intake of carbohydrates.
- Lack of physical inactivity. A sedentary life results in the accumulation of fat in your body, which can be a direct cause of increased blood glucose levels and, subsequently, insulin resistance.
- Excess lipid and fat accumulation around the waist, which inhibits the insulin’s action on the tissues around the waist, especially the liver. This condition is commonly observed in obese people. Men and women measuring 40 and 35 inches around the waist and higher, respectively, are more at risk.
- An increase in fatty acids, which causes an increase in lipid (triglyceride) synthesis. This causes changes in the liver, resulting in fatty liver and the liver’s resistance to insulin.
Additional possible causes include a family history of diabetes, smoking, alcoholism, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), ethnicity, endocrine disorders, age, certain medications, mental stress and more.
The potential causes above result in increased glucose production, or gluconeogenesis. When the body tries to compensate with the production of insulin, the beta (β) cells fail, eventually leading to Type 2 diabetes.
Recent studies have established the relation of insulin resistance to metabolic syndromes. Hypertension, for example, can also lead to insulin resistance.
How does Insulin Resistance Affect Type 2 Diabetes?
When the body develops insulin resistance, the beta cells of the pancreas start producing more insulin. While this compensates for the initial imbalance, the beta cells become worn out and cease to produce insulin. If an individual’s fasting glucose levels range between 100 and 125 mg/DL, this is considered prediabetes.
Proper exercise and a change in lifestyle help to prevent the progression from prediabetic to Type II diabetes. If uncontrolled, insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes can lead to complications including cardiovascular disease, renal disorders, reduced immunity, poor healing, and more.
Insulin resistance precedes Type 2 diabetes, and people with medical conditions such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and similar are more prone to these conditions than healthy people. The best way to prevent these conditions is to adopt a healthy diet and lifestyle.