Key Takeaways
- Intermediate action: steady basal coverage between meals.
- Peaks later than regular insulin; watch for lows.
- Cloudy suspension; gently roll before dosing.
- Mixing rules matter for safety and accuracy.
This guide explains nph insulin in clear terms and plain steps. You will see how it works, when it peaks, and how to handle it. We also cover storage, mixing, brands, and safety points. Use these basics to discuss a safe plan with your care team.
What Is NPH Insulin?
NPH stands for Neutral Protamine Hagedorn, a long-used intermediate-acting insulin. Clinically, it is isophane insulin, which combines insulin with protamine and zinc. This pairing delays absorption after injection. The result is a slower onset and a modest peak that can cover daytime or overnight basal needs.
People with type 1 diabetes often use it alongside rapid or short-acting insulin for meals. Some with type 2 diabetes may use it alone or with oral agents. Its time-action fits predictable routines but needs attention to meals and activity. Understanding its profile helps reduce hypoglycemia and variability.
Onset, Peak, and Duration
After subcutaneous injection, onset typically occurs in 1–2 hours. The intensity then rises, reaching a midcourse effect. Many patients experience the strongest effect several hours after dosing. Knowing this pattern helps align meals, snacks, and monitoring. Clinicians often teach patients to anticipate that midcourse effect during daily routines.
The expected nph insulin peak generally lands about 4–8 hours after dosing. Duration may extend 12–18 hours, though individual response varies. These ranges come from product labeling and clinical guidelines, which show wide variability between people. For a broader time-action overview, see Intermediate-Acting Insulin Types for context and charts.
For a framework comparing intermediate agents, see Intermediate-Acting Insulin Types for a time-action overview.
Clinical references summarize these ranges in standard teaching. For official time-action ranges, consult ADA insulin basics for plain-language guidance, and review FDA product labeling for detailed pharmacokinetics.
Comparing With Regular Insulin
Short-acting regular insulin starts faster and peaks sooner. It is commonly used for meals or correction doses. By contrast, the intermediate profile supports basal coverage. A combined plan can smooth daily glucose swings when meals and sleep are predictable. Matching each insulin’s role reduces overlap and gaps.
Understanding regular insulin peak helps you time meals and snacks. In many regimens, regular covers the meal rise while intermediate covers in-between times. If schedules vary, patterns can drift, causing lows or highs. For a clear primer on short-acting agents, see Regular Insulin Guide for how short-acting insulin behaves.
Mechanism and Pharmacology
Isophane formulations delay absorption by forming complexes with protamine and zinc. After injection, these complexes dissolve gradually in the subcutaneous tissue. The result is a prolonged and blunted rise in plasma insulin compared with unmodified forms. Temperature, injection site, and activity can shift the curve.
The nph insulin mechanism of action reflects the same cellular pathway as human insulin. It binds to insulin receptors, increases glucose uptake, and suppresses hepatic output. What differs is the delivery timing from the subcutaneous depot. For historical context on formulations, see Insulin Therapy Evolution to understand how basal strategies progressed.
Mixing and Combinations
Many legacy regimens use premixed combinations or patient-prepared mixes. When appropriate, clinicians may advise a fixed mix before breakfast and dinner. This approach may simplify routines for some, yet it reduces flexibility. Precision and consistent technique remain essential to avoid dosing errors and glycemic swings.
If your plan includes nph insulin and regular insulin, follow the mixing order taught by your care team. Typically, clear insulin is drawn up before cloudy insulin in a syringe. Premixes reduce steps but lock ratios. For format specifics, see Premixed Insulin Overview for how fixed ratios change timing.
Manufacturer and regulatory documents outline mixing and administration guidance. For formal instructions, review official product labeling for syringe order and compatibility details.
Dosing Timing and Administration Tips
Plans vary widely by individual needs, meals, and risk. Many people take an intermediate dose in the morning or at bedtime. Others use twice-daily dosing for smoother basal coverage. Whatever the plan, keep consistent timing and document patterns with a simple log.
Clarify when to give nph insulin relative to meals and activity. Structured timing helps reduce nocturnal lows or late-day dips. Discuss snack timing if your schedule shifts often. For practical examples across insulin types, see Insulin Types Guide to place NPH among other options.
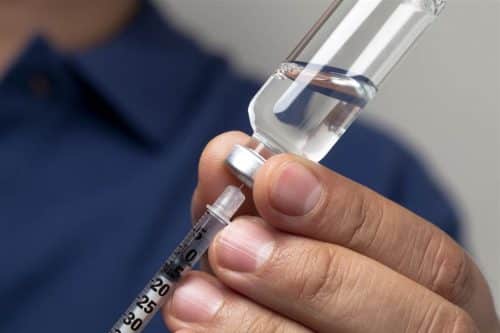
Appearance and Handling
This insulin is a suspension, not a clear solution. Proper resuspension helps dose accuracy and predictable absorption. Gently roll the vial or pen between your hands until evenly milky. Do not shake vigorously, which can foam and affect measurement. Always inspect the cartridge or vial before injecting.
If you wonder, is nph insulin cloudy, the answer is yes. It should look uniformly milky when ready. If you see clumps, crystals, or separation that does not mix, do not use it. Check expiration and storage history. For device-specific details, see Humulin N KwikPen for pen option details, including cartridge format.
Storage and Stability
Insulin potency depends on temperature, light, and time out of refrigeration. Unopened product generally stays refrigerated within labeled ranges. In-use pens or vials may be kept at room temperature within limits noted in labeling. Tracking dates and temperatures reduces variability and waste. Avoid leaving insulin in cars, near windows, or in direct heat.
Follow product labeling for nph insulin storage, including discard timelines. Always check the box insert for pen and vial differences. For a risk checklist on heat, freezing, and light, see Insulin Storage Dangers for storage thresholds and warning signs. Manufacturer and diabetes-organization pages also summarize stability guidance; see the ADA insulin basics for plain-language storage reminders.
Brands and Formulations
Several human isophane formulations remain available in vials and pens. Common examples include Humulin N and various Novolin isophane products. Concentrations typically are 100 units/mL. Delivery forms include vials, penfill cartridges, and prefilled pens. Selection depends on preference, dexterity, and training.
To compare vial options and concentrations, see Novolin Ge NPH Vials for vial formats and concentrations. If you prefer pens for ease of dialing, review Humulin N KwikPen for pen device specifics. For broader reading, visit Diabetes Articles to explore approach and therapy topics.
Safety, Side Effects, and Precautions
All insulins can cause hypoglycemia, which may be severe. Signs include shakiness, sweating, hunger, and confusion. Always carry a rapid carbohydrate and know your response plan. Consider a medical ID if you have a history of severe lows. Alcohol and exercise can increase your risk at peak times.
Other effects may include injection-site reactions and mild edema. Rarely, allergic reactions may occur. Discuss past reactions, renal or hepatic impairment, and other comorbidities with your clinician before changes. Review medication lists for interactions that may blunt awareness of lows. For a general overview of medication classes, see Diabetes Medications Overview to understand adjunct treatments.
Choosing Alternatives and Adjuncts
Some patients transition to long-acting analogs for flatter profiles. Others retain intermediate regimens due to routine, preference, or cost considerations. The best plan balances safety, predictability, and simplicity. Any switch should include education on new timing, monitoring, and hypoglycemia risk.
To compare basal analogs with different kinetics, see Lantus Half-Life for kinetics background, and Toujeo vs Lantus for differences within one analog family. For type-specific education resources, browse Type 1 Diabetes or Type 2 Diabetes to align learning with your diagnosis.
Recap
NPH offers intermediate coverage with a delayed rise and defined peak. Consistent technique, timing, and storage support stable outcomes. Pair its profile with meals, activity, and monitoring for safer daily use.
Note: Product labels and clinical guidelines evolve. Review the latest official documents and professional advice before making changes.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.